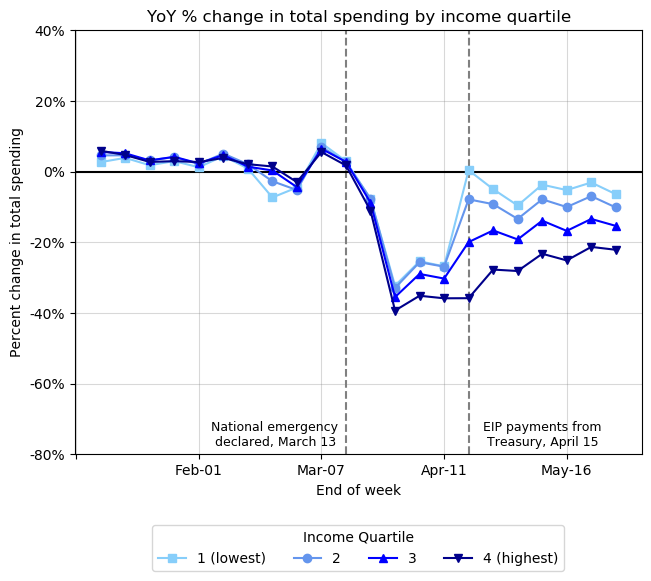
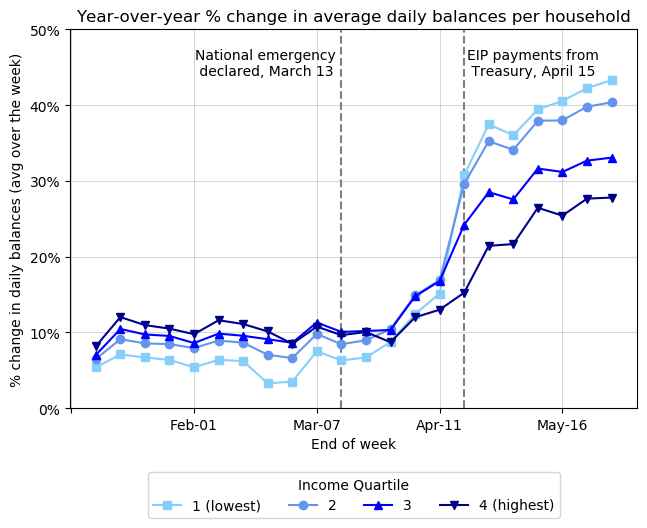
While households who entered the pandemic with low levels of cash on hand saw their checking account balances shoot up around the time stimulus payments were received, our analysis reveals that balances soon began to decline, suggesting that the additional funds have been used up fairly rapidly.
Perhaps surprisingly, we find that lower-income families drove a larger share of the overall increase in savings seen across income levels. While higher-income families saved more in dollar terms, the disproportionate share of increasing savings for lower-income families means a shift in the distribution of wealth towards lower-income households. Liquid wealth inequality decreased between February and May—implying an almost two percentage point decline in the share of liquid wealth held by the highest-income families.
Why it Matters:
As policymakers consider how to support economic recovery most effectively, it will be important to continue watching what happens to families’ levels of spending and savings. While it may be too soon to draw hard conclusions, there is reason to think that the gains in wealth distribution for lower-income families may not be permanent and the pandemic could have impacts on savings that, overall, exacerbate the wealth gap that existed before the crisis. Absent additional government stimulus, households who face job loss may need to spend what they have saved (or take on debt) just to keep up with bills and necessary expenses, whereas those with job security still receive income and may save more than they would otherwise just by nature of there being fewer places open to spend.
Finally, Institute research has repeatedly demonstrated the importance of liquid savings for maintaining financial resilience during times of uncertainty, and this recent report demonstrates the meaningful role for government support in stabilizing financial disruptions that families have experienced during the current pandemic.
The disproportionate increase in savings seen from lower-income families, for example, very likely reflects the fact that stimulus checks and expanded unemployment insurance benefits provided a substantially more important income cushion for lower-income households than higher-income households. Depending on the extent to which these disruptions continue, policymakers need to consider that more funding to lower-income families may be necessary to maintain their spending and prevent hardship.
These findings draw from a longer paper which was released as part of the Brookings Papers on Economic Activity, on June 25, 2020. Read more of the Institute's research here.